What Are Valence Quarks Made Of
These include the mesons which get their quantum numbers from a quark and an antiquark and the baryons which get theirs from three quarks. We show furthermore that the data are compatible with uncorrelated behaviour of the valence quarks of the incident proton each of them having a probability 06 to emerge in the fragmentation baryon B and a probability 04 to emerge in a meson.
 How Can The Proton Include Top Quarks If A Top Quark Is Heavier Than The Proton Physics Stack Exchange
How Can The Proton Include Top Quarks If A Top Quark Is Heavier Than The Proton Physics Stack Exchange
For the proton these are one down quark and two up quarks.
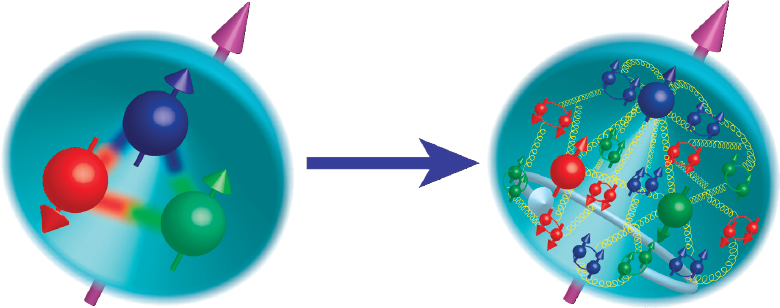
What are valence quarks made of. Protons contain two u and one d. The naming is based on the valence electrons of atomic physics which are essentially responsible for the chemical properties of the atoms. Protons contain two u and one d.
Gluons can dissociate into quarkantiquark pairs sea quarks and can also interact with other gluons normal quarks are shown here in red antiquarks in blue. From previous experiments scientists knew that only valence quarks can grab major portions of a nucleons total energy content says Jian-Ping Chen of the Jefferson lab a coleader of the experiment. In addition to those so-called valence quarks each nucleon contains multitudes of gluons--particles that bind quarks --and of short-lived quark-antiquark pairs known collectively as the quark sea.
All commonly observable matter is composed of up quarks down quarks and electrons. Intriguingly this is made up of 65 from up-valence and 35 from down-valence quarks. Only three unbalanced valence quarkstwo ups and a downcontribute to the protons overall charge.
The quarks and antiquarks which impart quantum numbers to hadrons are called valence quarks. Magnetic moments of valence constituent quarks. Valence quarks or constituent quarks are quarks that determine the most important properties of a Hadron such as mass momentum electric charge and spin.
The three valence quarks come in two types flavours up u quarks and down d quarks. µn 1 3 4µd µu. A quark kwɔːrk kwɑːrk is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter.
µp 1 3 µd 22µu µd 1 3 4µu µd Paired quarks of the same flavour and opposite spin cancel The neutron magnetic moment follows from isospin symmetry. When two or more quarks are held together by the strong nuclear force the particle formed is called a hadron. Quarks that make the quantum number of hadrons are named valence quarks.
Each valence quark interacts with another through a gluon. In particle physics the quark model is a classification scheme for hadrons in terms of their valence quarksthe quarks and antiquarks which give rise to the quantum numbers of the hadrons. Each valence quark interacts with another through a gluon.
Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons the most stable of which are protons and neutrons the components of atomic nuclei. The two families of hadrons are baryons made of three valence quarks and mesons which are made from a quark and an antiquark. The composite particles made of quarks and antiquarks are the hadrons.
Protons contain two u and one d. Fundamental particles called quarks and gluons. The three valence quarks come in two types flavours up u quarks and down d quarks.
µ 2µqSz where µu 2e 3mu 2µN µd e 3md µN Starting from the proton flavourspin wavefunction see above. The three valence quarks come in two types flavours up u quarks and down d quarks. It is now established that about 30 of the proton spin is in the valence quarks.
The quark model underlies flavor SU or the Eightfold Way the successful classification scheme organizing the large number of lighter hadrons that were being discovered starting in the 1950s and continuing through the 1960s. Models made different predictions for how the ratio of down and up antiquarks. The sea seems to be unpolarised and about 20 of the protons spin is in gluon polarisation though it is not possible to measure this accurately across a wide kinematic range.
It received experimental verification beginning in the late 1960s and is a.
 Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Quantum Mechanics Physics And Mathematics Physics
Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Quantum Mechanics Physics And Mathematics Physics
 S U P E R S T R A N G E L A N D Quantum Physics Simplified Quantum Physics Physics Physics And Mathematics
S U P E R S T R A N G E L A N D Quantum Physics Simplified Quantum Physics Physics Physics And Mathematics
 3 Mrk 600x793 Jpg 600 793 Science Art Scientific Illustration Art Prints
3 Mrk 600x793 Jpg 600 793 Science Art Scientific Illustration Art Prints
 Theory Argonne National Laboratory
Theory Argonne National Laboratory
 Why Doesn T Antimatter Anti Gravitate Protons Mass Electrons
Why Doesn T Antimatter Anti Gravitate Protons Mass Electrons
 Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Black Hole Modern Physics
Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Black Hole Modern Physics
 Large Hadron Collider A Smashing Record Physics Large Hadron Collider Physics And Mathematics
Large Hadron Collider A Smashing Record Physics Large Hadron Collider Physics And Mathematics
 Exploring The Proton Sea Science
Exploring The Proton Sea Science
 The Atomic Nucleus Scientific Illustration Science Art Illustration
The Atomic Nucleus Scientific Illustration Science Art Illustration
 Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Protons Physics Theoretical Physics
Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Protons Physics Theoretical Physics
 Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Quantum Mechanics Science
Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Quantum Mechanics Science
 Valence Electrons And Chemical Bonds Chemical Bond Physical Science Science Chemistry
Valence Electrons And Chemical Bonds Chemical Bond Physical Science Science Chemistry

How Many Quarks Are In A Proton I Ve Heard That There Can Be Hundreds Of Virtual Quark Antiquark Pairs At Once But Only Three Valence Quarks Quora
 Physicists Find Signs Of Four Neutron Nucleus Physicists Protons Neutrons
Physicists Find Signs Of Four Neutron Nucleus Physicists Protons Neutrons
 Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Quantum World Physicists
Why Does The Proton Spin Physics Holds A Surprising Answer Physics Quantum World Physicists
 Valence And Core Electrons Chemwiki Physical Science Electrons Core
Valence And Core Electrons Chemwiki Physical Science Electrons Core
 Strong Forces Make Antimatter Stick Nanotechnology Physicists Simple Math
Strong Forces Make Antimatter Stick Nanotechnology Physicists Simple Math
 1 Introduction An Assessment Of U S Based Electron Ion Collider Science The National Academies Press
1 Introduction An Assessment Of U S Based Electron Ion Collider Science The National Academies Press